Sub-Saharan Africa
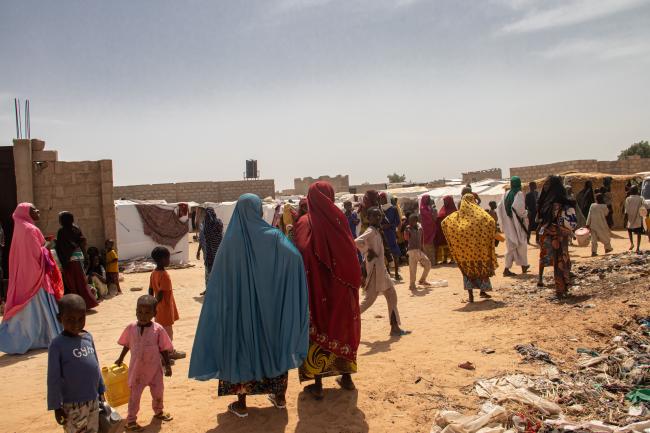
Sub-Saharan Africa is not monolithic. While crises in the Sahel have attracted a great deal of attention, other regions also need to be monitored, and not just through the prism of security.
Related Subjects
Nigeria’s 2023 Election: Democratic Development and Political Fragmentation
Nigerians will go to the polls on February 25 to elect a new president and members of the National Assembly. This marks the 7th in an unbroken sequence of presidential elections held since the country’s return to democracy in 1999.
The Politics of New Cities: Diversification of Actors and Recentralization of State Power in the Case of Diamniadio
The construction of new cities on the African continent is in vogue. From multifunctional urban hubs to eco-districts, the images that accompany the announcement of these projects promote an African urban future based on modernity and technology.
Self-defense Groups, the Pyromaniac Firefighters of Sahel
Since 2012, the proliferation of jihadist groups across the Sahel has monopolized the attention of the authorities.forced by the threats they represent and the weakening of their regal power, states are gradually withdrawing from their peripheral rural territories. As a result, populations have organized themselves to become local security providers.
The Roots of a Quarter-Century of Violence Lie to the East of Congo (Kinshasa)
Almost thirty years after the genocide of the Tutsis in Rwanda, the entire region remains unstable. After Paul Kagame came to power, 1.5 million Hutus fled to the Democratic Republic of the Congo. For the Rwandan president, they represented an unacceptable threat. There then followed the First and Second Congo Wars, the consequences of which are still apparent. The recent attacks perpetrated by the M23 rebels are a new episode in this tragic story.
China in Madagascar: Between Quiet Politcal Oppurtunism and Intense Trafficking
In the context of growing regional rivalries between major powers in the Indian Ocean, the stakes of Sino-Malagasy relations are major.
Chinese Influences in Africa 2. Myths and Realities in Economic Relations
China and Africa share a strong relationship since the wave of African independences in the 1960s. Nevertheless, China-Africa trade has experienced an unprecedented surge since the late 1990s and has been accompanied by the rise of a discourse of "win-win" partnership between China and Africa.
New Paradigm for Electrification in Sub-Saharan Africa: How Are Decentralized Hybrid Systems Changing the Game?
After several decades of reforms, the situation in centralized power sectors has hardly changed. The sub-Saharan power sector remains underdeveloped, and power sectors are experiencing significant financial difficulties that have been further exacerbated first by the effects of the pandemic and then the war in Ukraine.
Japan’s Africa policy: Back to basics in times of crisis
Addressing remotely the 8th Japan-Africa TICAD Summit held in Tunis between August 27th and 28th, Japanese Prime Minister Fumio Kishida pledged $30 billion in public and private contributions to the African continent over the course of the next three years. This is a quite a remarkable move, as no specific amount was mentioned by the late Prime Minister, Shinzō Abe, at the previous TICAD 7 in 2019. By doing so, Japan aims at demonstrating that its commitment to Africa is solid and sustainable: its traditional approach towards a human-centered development is more relevant than ever in these times of crisis (between the pandemic, the war in Ukraine, and the adverse effects of climate change), and clearly marks a difference from China’s practices.
Mbororo Fulanis in the Anglophone Crisis: From Land Disputes to a Regional Conflict
This study highlights the particular situation of the Mbororo minority, which has settled in the Northwest English-speaking province that is more conducive to livestock farming than the Southwest.

Japan steps up its Africa engagement
Laying the foundation for the Eighth Tokyo International Conference on African Development (TICAD), Japanese Foreign Minister Yoshimasa Hayashi held talks on 28 March 2022 with ministers from 50 African nations. Hayashi expressed concerns that the COVID-19 pandemic and the war in Ukraine had increased the economic and social vulnerabilities of African countries — deepening their dependence on China. He subsequently committed to increase Japan’s cooperation with Africa.
Defining the Middle Class in the Global South. A Quantitative Perspective from South Africa
What makes you middle class? Is it your income, occupation, or education? Your family background or maybe the house and neighbourhood you live in? It is probably all of these things.
The Resurgence of Conflict in Mozambique. Ghosts from the Past and Brakes to Peaceful Democracy
2016 proved to be a most challenging year for Mozambique. Small-scale conflict, which started reappearing between the government and the opposition party, the Mozambican National Resistance (Renamo), in 2013, intensified over the course of the year, whilst peace negotiations stalled.
Africa and the ICC Going Forward
October 2016 presented a grim test for the fourteen-year-old International Criminal Court (ICC) as three Sub-Saharan African countries, Burundi, South Africa and Gambia announced their decision to opt out of the international judicial body.
Robert Mugabe in Zimbabwe: the Endgame?
The descent into the morass of failure seems relentless for a country that used to be, at the aftermath of its independence in 1980, the “jewel in Africa” to be carefully preserved, as former Tanzanian President Julius Nyerere advised an acclaimed Mugabe ascending into power.
South African Local Elections 2016. From One Party Dominance to Effective Plural Democracy
The South African political landscape experienced a shock from an unlikely source; the country’s local government elections on August 3, 2016 representing the last tier of government and often overlooked in favour of national and provincial polls.
Not Dazzling But Not Invisible : The Ugandan Middle Classes as "Somewhere in Between"
In January 2016, the Kenyan supermarket chain Uchumi has filed bankruptcy for its Ugandan subsidiaries, due to perpetual losses. And they are not alone: companies like Nestlé, Coca Cola or Barclays are slowly pulling out of Africa and recent reports – such as the Global Wealth Databook from Credit Suisse or from the Pew Research Center – suggest that the size of the African middle class may be much smaller than previously thought. So was the hype in recent years about “Africa rising” (Mahajan, 2009) and the African middle class just a bubble? In order to better comprehend the social and economic transformations taking place on the continent, it can prove helpful to look beyond the dazzling facade of economies such as Kenya or South Africa, and into those countries experiencing steady growth, but nevertheless far from including a well established middle class. Their middle classes are not shopping in big malls, driving cars and going on holidays. Rather, these groups are characterized by the improvement of their livelihoods compared to their parents’ generation, in terms of education, income and housing, but they still feel strongly vulnerable, and do not take their new benefits for granted. This has an important effect on their consumption patterns, and may not turn them into the promising new consumers, as they have sometimes been praised to be.
Determinants of Japan’s ODA Allocation in Africa
The debate on emerging donors raises a question whether traditional donors really follow their own ODA (Official Development Assistance) policies or not. This paper addresses the question by investigating Japan’s adherence to its own ODA policies.
Fragility Factors and Reconciliation Needs in Forest Guinea
In December 2013 the first Ebola cases surfaced in Guéckedou district, near the Liberian and Sierra Leon borders in the Forest Region of Guinea. The outbreak quickly spread from Forest Guinea to the rest of the country and, through the borders, to neighbouring countries. It took three months to identify the Ebola virus as the causative agent of the burgeoning epidemic, longer for the Guinean government to understand the importance of treating the outbreak as a national emergency, and even more time for everyone involved to appreciate the great social toll of Ebola.
France and the Fight against Terrorism in the Sahel: The History of a Difficult Leadership Role
Except for its extreme poverty and the disastrous effects of a series of droughts, the Sahel region has been largely out of the spotlight of international attention in the past. Yet the rise of terrorism and especially the creation of Al-Qaida in the Islamic Maghreb (AQIM) in 2007 brought the region into the focus of world politics. Initially, AQIM"s activities in the Sahel mainly posed a threat to the stability of the Sahelian states themselves. In an effort to internationalize its agenda, however, AQIM also started targeting Western countries.
A Class Defined "by Consumption": The Grocery-Shopping Practices of the Lower-Middle Classes in Johannesburg, South Africa
The black middle class in Johannesburg is a much debated but ill-defined phenomenon, treated more often by economic players than by social scientists. Far from static and clear, the concept of the middle class is for us relevant insofar as it reveals crucial dynamics of the society.
Support independent French research
Ifri, a foundation recognized as being of public utility, relies largely on private donors – companies and individuals – to guarantee its sustainability and intellectual independence. Through their funding, donors help maintain the Institute's position among the world's leading think tanks. By benefiting from an internationally recognized network and expertise, donors refine their understanding of geopolitical risk and its consequences on global politics and the economy. In 2025, Ifri supports more than 80 French and foreign companies and organizations.